By MIA Professional Practices & Technical Team
Survey Highlights:
- 52% and 36% of survey respondents propose to adopt data analytics tools and artificial intelligence (AI) respectively in the next three years, signalling the effectiveness of MIA’s advocacy for the profession’s digital transformation
- 93% of survey respondents ranked technology as either very important or important, and 92% of respondents said that they were either very interested or interested in knowing more about technologies affecting the accountancy profession
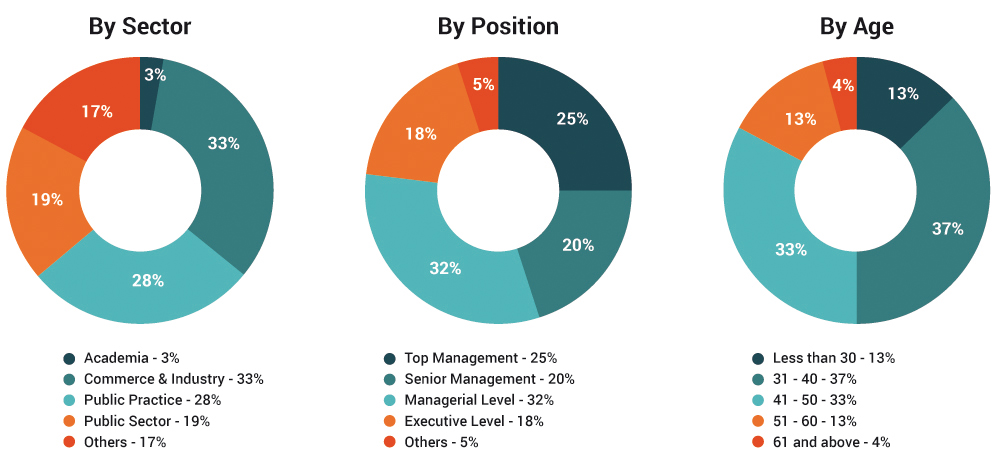
- Diverse opinions were recorded from a total of 1,126 respondents across the four sectors of the MIA membership, who are well-balanced in terms of sector, position and age
To support MIA’s digital advocacy, a survey on ‘Technology Adoption by the Accountancy Profession in Malaysia 2019’ was conducted between July and November 2019.
This 2019 survey is a follow up to a similar survey that was carried out in 2017 which contributed to the development of the MIA Digital Technology Blueprint that was launched in July 2018. Its findings can be accessed at https://www.mia.org.my/v2/downloads/resources/publications/2018/07/12/MIA_Technology_Blueprint_Spreads_format.pdf
A total of 1,126 respondents across the four sectors of the MIA membership provided feedback on their adoption of technology on the following:
- Their breadth and depth of knowledge about technology;
- The technology trends affecting members;
- Drivers and barriers in adopting technology; and
- How members are applying technology in their organisation.
The respondents are well-balanced and offer a diversity of backgrounds and opinions. In terms of sector, there is a mix of respondents from commerce and industry (33%), public practice (28%), public sector (19%) and others (17%). In terms of position, 25% are from top management and 20% from senior management, indicating that a high percentage of respondents hold decision-making powers. In terms of age, there is also a balanced mix of digital immigrants (those who were not exposed to technology from young) and digital natives (those who have been interacting with technology since childhood).
Highlights of survey findings
Below are the highlights of the survey findings, with comparisons between the 2019 and 2017 survey data:
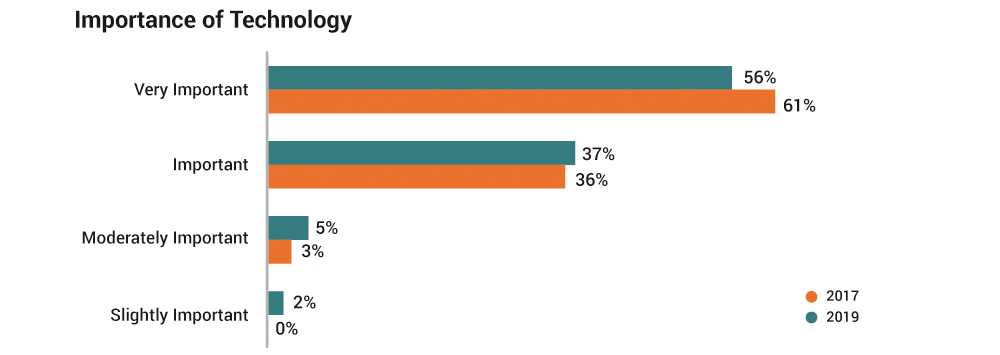
- Overall, respondents remain confident that technology is very important (93% of 2019 survey respondents ranked technology as either very important or important compared to 97% of the 2017 survey respondents).
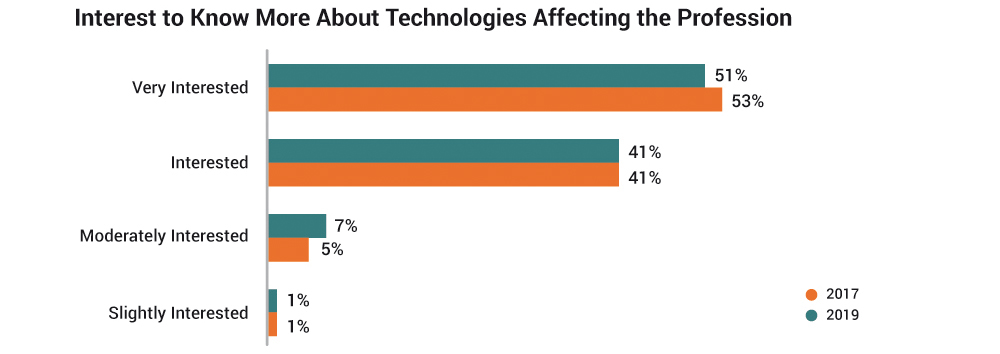
- Respondents also expressed interest in learning more about the technologies affecting the profession (92% of 2019 survey respondents said that they were either very interested or interested in knowing more, compared to 94% of the 2017 survey respondents).
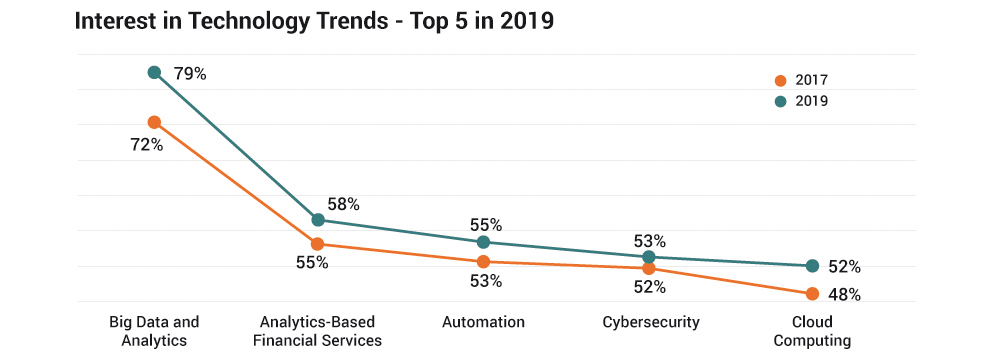
- Respondents to the 2019 survey showed greater interest in technology trends, where they were most interested in the following top five trends ranked from first to fifth: big data and analytics (2019 – 79%: 2017 – 72%), analytics-based technologies (2019 – 58%: 2017 – 55%), automation (2019 – 55%: 2017 – 53%), cybersecurity (2019 – 53%: 2017 – 52%) and cloud computing (2019 – 52%: 2017 – 48%).
- However, respondents’ interest in technology trends differed from respondents’ perception of the key technologies affecting the profession. Respondents ranked the following technologies as those with higher impact on the profession, and there was also an increase in the number of respondents who cited these technologies as affecting the profession: first, cybersecurity (2019 – 71%: 2017 – 72%), followed by big data and analytics (2019 – 69%: 2017 – 64%), online services (2019 – 65%: 2017 – 61%), automation (2019 – 64%: 2017 – 62%) and analytics-based financial services (2019 – 64%; 2017 – 57%).
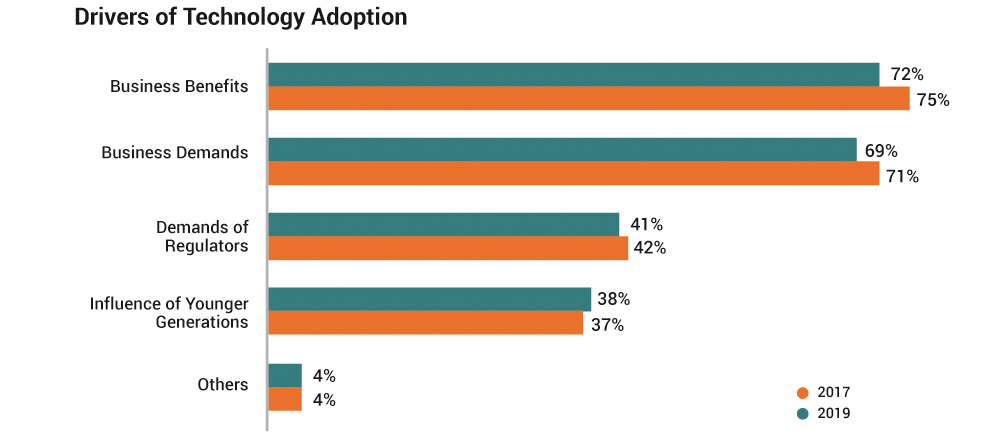
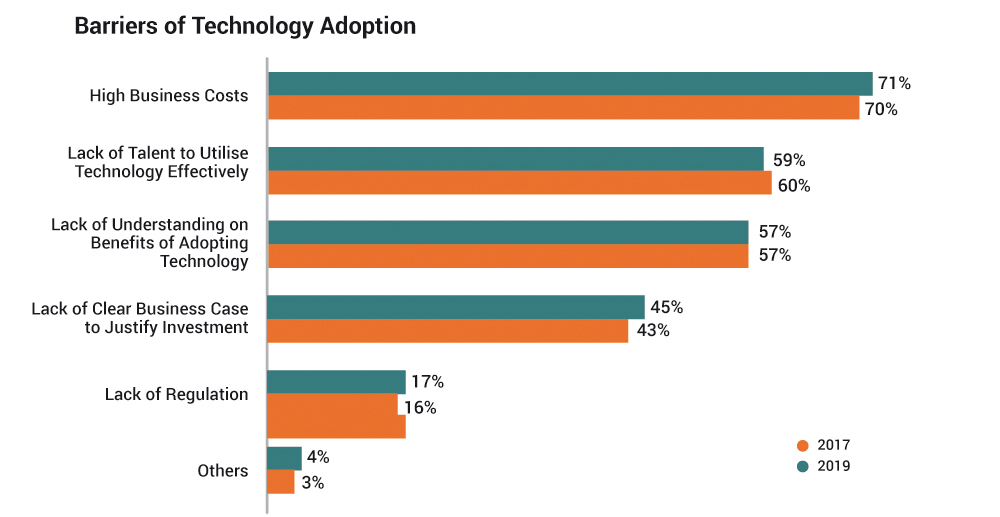
- There was little change in the perception of drivers and barriers to technology adoption (table 4). Business benefits (2019 – 72%: 2017 – 75%) and business demands (2019 – 69%: 2017 – 71%) were cited as the top drivers of technology adoption while high business costs (2019 – 71%: 2017 – 70%) ranked as the main barrier to adoption, followed by lack of talent to utilise technology effectively (2019 – 59% : 2017 – 60%) and lack of understanding on benefits of technology adoption (2019 – 57%: 2017 – 57% ).
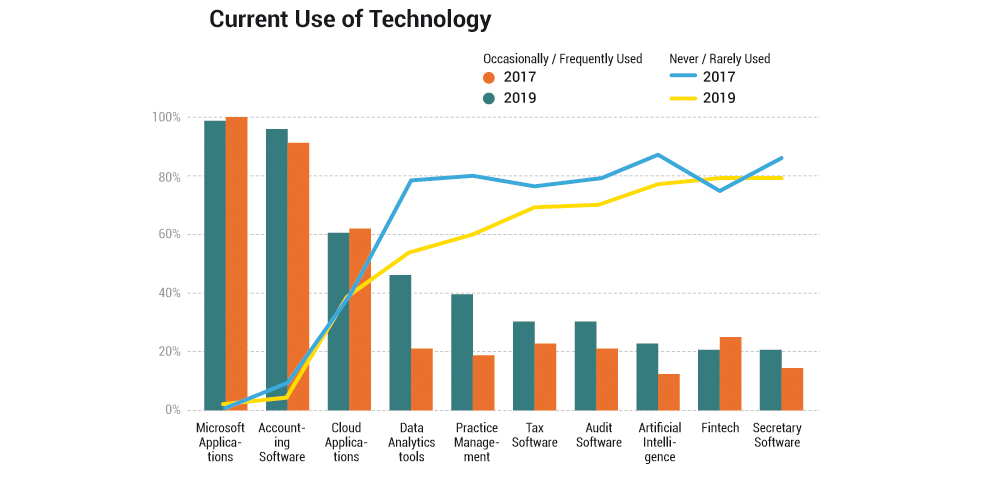
- In terms of frequency of usage, respondents indicated that Microsoft applications (nearly 100% report use), accounting software (over 90% report use) and cloud applications (about 60% report use) are currently used the most pervasively.
- Interestingly, respondents are now more exposed to data analytics tools, as indicated by the number of respondents who have never or rarely used data analytics tools having plunged from 79% in the 2017 survey to under 60% in the 2019 survey. This indicates a greater take-up of data analytics tools, as over 40% of 2019 respondents said they now frequently or occasionally use data analytics, double the 20% of 2017 respondents who confirmed frequent or occasional use.
- There is also increased usage of practice management software. Those who have never or rarely used this software dropped from 81% of 2017 respondents to 60% of 2019 respondents, while those who occasionally and/or frequently use it rose to 40% of 2019 respondents, double the 19% of 2017 respondents. This could signal a growing emphasis on audit quality and practice transformation, but there is plenty of room for further adoption of practice management software to enhance practice business continuity and sustainability.
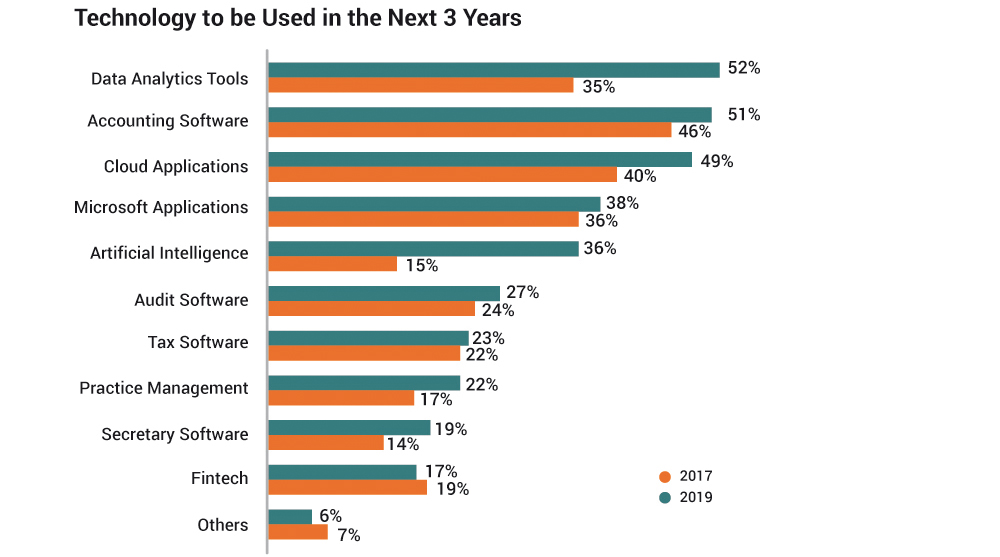
- In the next three years, the 2019 survey respondents expect to increase their adoption of data analytics tools (52%), accounting software (51%), and cloud applications (49%). Notably, survey respondents express increased interest in adopting data analytics tools (52% – 2019: 35% – 2017) and artificial intelligence tools (36% – 2019: 15% – 2017). This could indicate that MIA’s advocacy and exposure of members to digital transformation and technology leveraging has been effective. MIA will continue to work harder to strengthen the profession’s digital transformation.
Implementation of the Blueprint
The Institute, through its Digital Technology Implementation Committee (DTIC), has developed an operational plan to implement the Blueprint, focusing on the principles set out in the Blueprint as follows:
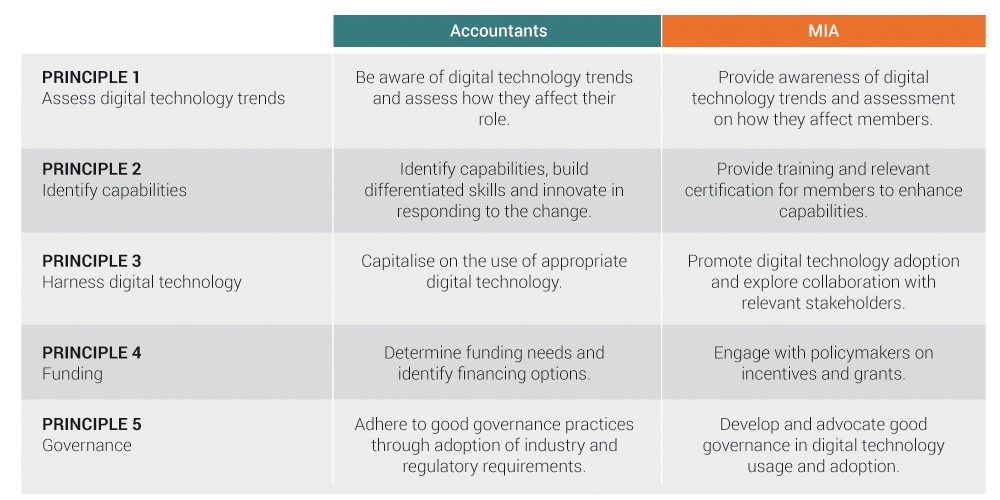
The findings of this survey are being used in the implementation of the operational plan of the Blueprint. MIA extends its deepest appreciation to the members who have responded to the survey. The Institute hopes that the ongoing implementation and operationalisation will be helpful to members in driving digital transformation, and encourages everybody to continue applying the five principles of the MIA Digital Technology Blueprint.







