By MIA Sustainability, Digital Economy and Reporting Team
The Malaysian Institute of Accountants (MIA) has undertaken the fourth iteration of the Survey on Technology Adoption by the Accountancy Profession in Malaysia in 2025 (Survey).
Since its inception in 2017, the Survey has laid the groundwork for the launch of the MIA Digital Technology Blueprint in 2018 and shaped subsequent initiatives for the Blueprint’s operational plans through the 2019 and 2022 editions. The 2022 Survey conducted in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic offered valuable insights into how the profession responded to the accelerated pace of digitalisation brought about by unprecedented global disruption.
Now, in 2025, the fourth Survey is at a pivotal juncture—capturing the trajectory of digital progress since 2022. The findings will not only reflect how the profession is adapting to technological advancement but also support MIA in charting the next phase of strategic initiatives to strengthen digital capabilities of the profession.
The 2025 Survey conducted from 1 November 2024 to 31 January 2025 captured responses from 713 MIA members across a diverse cross-section of the Malaysian accountancy profession as shown below.
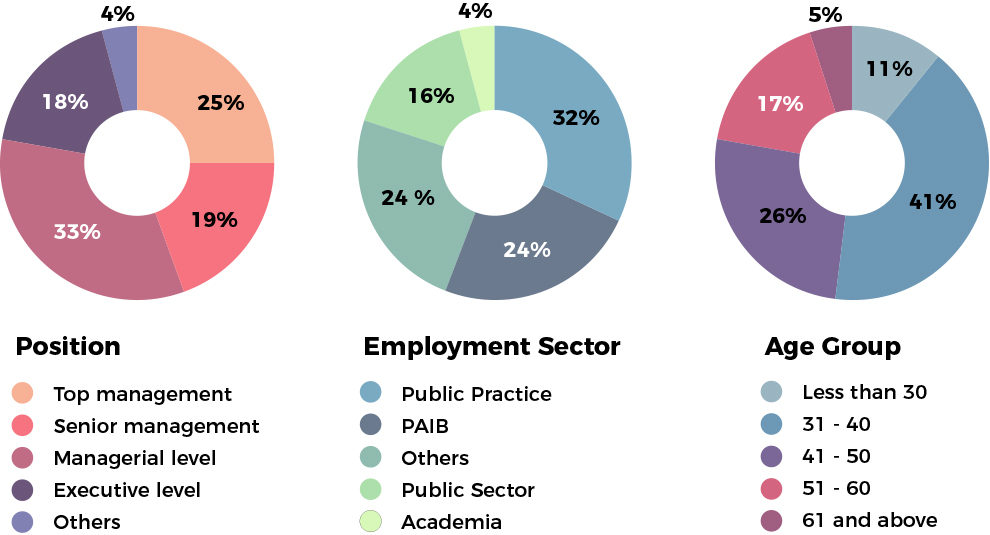
Figure 1: Demographic of survey respondents
From Adoption to Impact: How Technology Is Shaping the Profession
As the profession continues to evolve in response to rapid technological change, the 2025 Survey explored critical dimensions such as key technology trends affecting the accountancy profession, level of technology deployment and extent of impact that these technologies had on the profession.
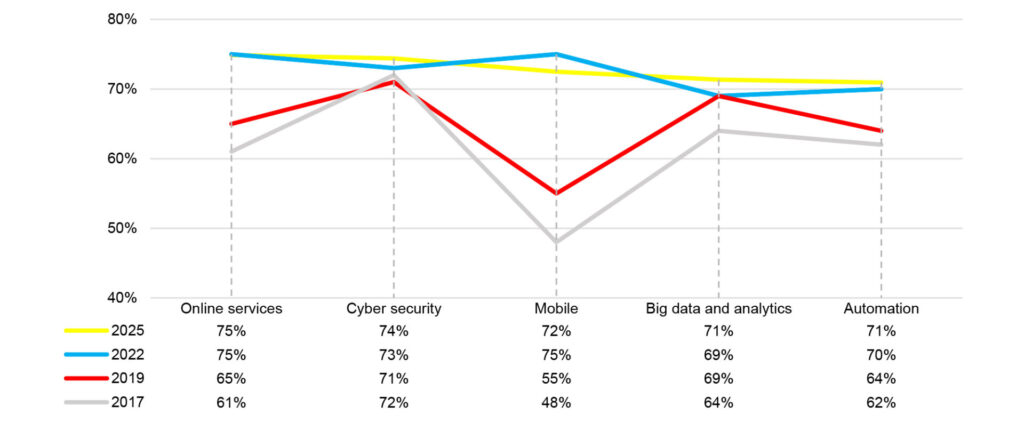
In 2025, respondents ranked the following technologies as having a greater impact on the profession with results largely consistent with – if not slightly exceeding or falling below – those from 2022. Compared to earlier years (i.e., 2019 and 2017), the data reflects a clear upward trend, especially in mobile technologies and automation, underscoring the profession’s ongoing digital advancement. Notably in 2025, cloud computing and data standards (e.g. XBRL, the data standard for financial reporting) also ranked highly among impactful technology trends.
The Survey reveals varying stages of deployment for different technologies among the Survey respondents.
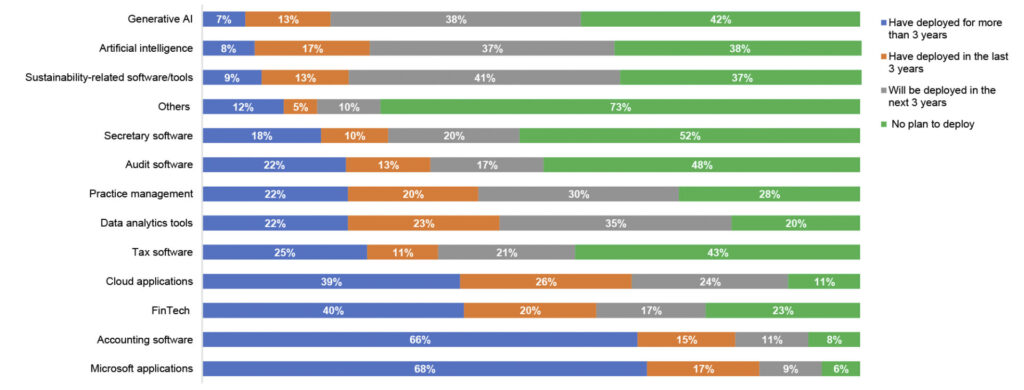
- Microsoft applications and accounting software are the most widely-deployed technologies, with 68% and 66% of respondents already using them for over 3 years.
- Cloud applications (26%) and data analytics tools (23%) show a higher percentage of deployment in the last 1-3 years compared to other technologies.
- Strong future interest exists in sustainability software/tools (41%), generative AI (38%), and artificial intelligence (37%), as many respondents plan implementation within the next three years, indicating a growing focus on these fields.
Expanding on the earlier insights into technology deployment, the following chart presents the extent of impact experienced across key sectors—Professional Accountants in Business (PAIB), Public Practice, Public Sector, and Others—following technology adoption.
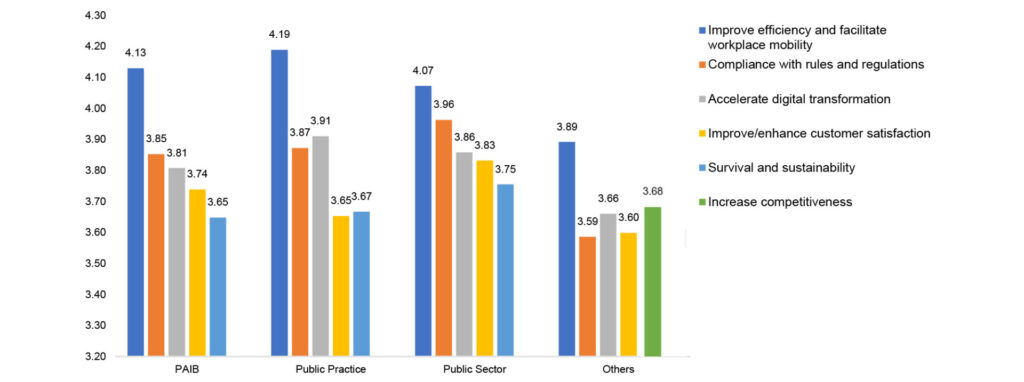
Across sectors, ‘Improve efficiency and facilitate workforce mobility’ consistently ranks as having a high impact following technology adoption, notably peaking in PAIB and Public Practice. This is followed by ‘Compliance with rules and regulations’ and ‘Accelerating digital transformation’. Conversely, in the category of Others, ‘Increase competitiveness’ appears for the first time as one of the top five impacts experienced by organisations after adopting technology.
State of Technology Adoption and Its Key Impediments
To provide insight into the extent of technology adoption, Figure 5 presents the stages reported by respondents in 2025, with 2022 data included for contextual reference.
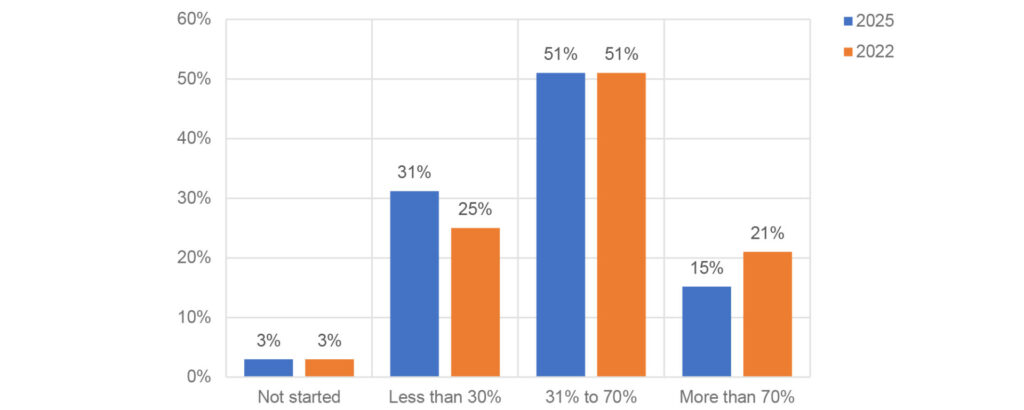
97% of respondents reported being in various stages of technology adoption, while only 3% had not commenced any adoption. This overall pattern mirrors the findings from 2022, signalling a sustained commitment to digital adoption across the profession. However, a closer look reveals a redistribution within the adoption spectrum. Notably, there is an increase in respondents at the earliest stage of adoption (less than 30%) while those in the high range (more than 70%) have declined.
Understanding the progress of technology adoption naturally leads us to consider the hurdles organisations encounter in adopting technology.
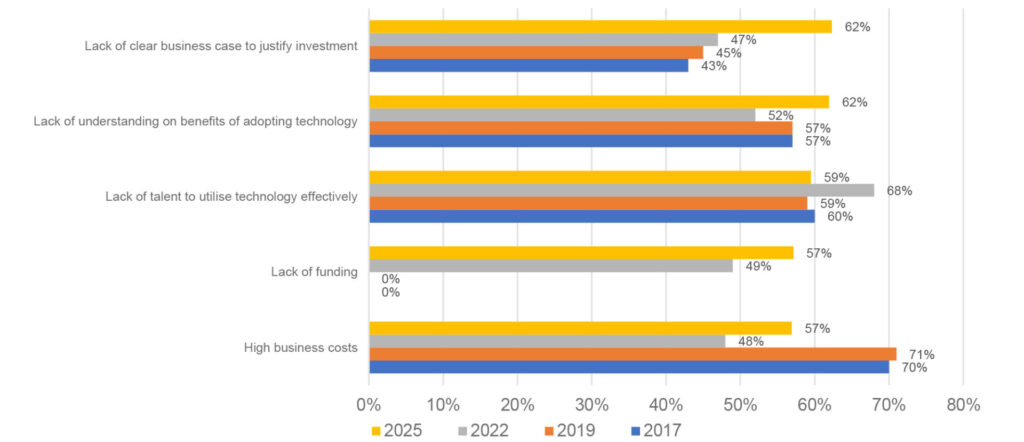
A notable shift in the barriers to technology adoption emerged in 2025, with the absence of a clear business case to justify investment now ranked as the primary obstacle—surpassing its position in 2022. This shift underscores an increasing awareness on the importance of understanding and aligning technological investments with tangible business outcomes.
Meanwhile, ‘understanding the benefits of technology’ and ‘lack of talent to utilise it effectively’ remained as consistent barriers over the years. However, the overall results show that funding is now a lesser concern, ranking fourth among key barriers, compared to third in 2022. Interestingly, while the percentage citing high business costs increased in 2025, it has become less of a deterrent compared to 2019 and 2017 suggesting that organisations may be more willing to invest in technology. This trend is further supported by the findings of the Survey, where only 11% of respondents did not allocate any budget for technology adoption in their organisation.
The Way Forward: Strengthening the Profession’s Digital Future
The Survey findings reaffirm that digital transformation remains an essential catalyst for progress across the Malaysian accountancy profession. While the profession has made steady strides in adopting impactful technologies, the journey is far from complete.
MIA will continue to play a central role in guiding the profession through its digital evolution. Insights from the Survey will help shape upcoming strategic initiatives aimed at fostering a future-ready accountancy profession. MIA extends its deepest gratitude to the members for their valuable input and participation in this Survey. The Institute hopes that both ongoing and future digital initiatives will be instrumental in driving digital transformation for our members.








