By Rasmimi Ramli
In 2016, the Ministry of Finance issued a letter to all federal statutory bodies (FSBs), encouraging the application of the Malaysian Public Sector Accounting Standards (MPSAS) in their financial statements. Gradually, FSBs are moving from their existing accounting framework which could be either the Malaysian Financial Reporting Standards (MFRS) or the Malaysian Private Entities Reporting Standard (MPERS) to MPSAS.
While the majority of FSBs have successfully moved to MPSAS, there are those that will either not move to MPSASs due to specific reasons or they happen to be at an early stage of their MPSAS implementation. This article provides an overview of the steps to be taken in implementing MPSAS by a FSB.
MPSAS 33, First-time Adoption of Accrual Basis Malaysian Public Sector Accounting Standards (MPSASs) provides guidance to a first-time adopter that prepares and presents financial statements under MPSAS. The diagram below shows the step-by-step application of MPSAS 33 by a first-time adopter transitioning to MPSAS.
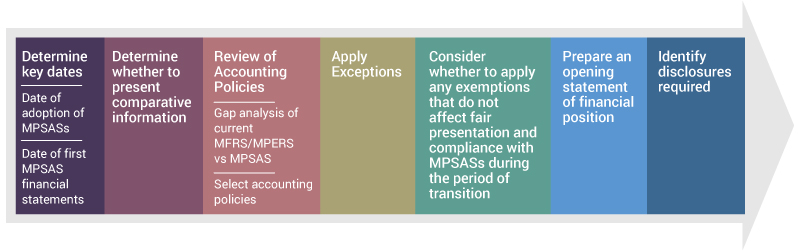
Determine key dates
Firstly, the FSB needs to determine the date of adoption of MPSASs¹ as well as the first MPSAS financial statements. This can be illustrated as follows:
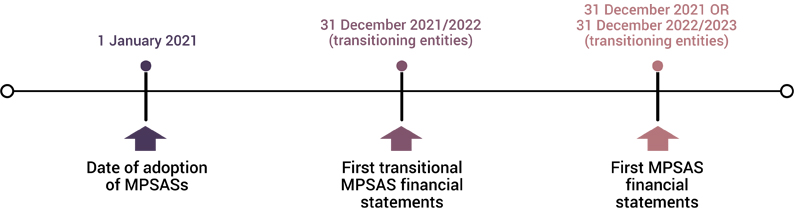
FSB X determines that its date of adoption of MPSASs is 1 January 2021. If it does not apply the exemptions available to first time adopters that affect fair presentation and compliance with MPSAS, its first MPSAS financial statements² would be on 31 December 2021. However, if it does, it produces its first transitional MPSAS financial statements³ on 31 December 2021 and continues to produce transitional MPSAS financial statements until the exemptions have expired i.e. when the 3-year transitional relief period ends and/or when it complies with all MPSASs requirements (whichever is earlier). This article does not cover such exemptions.
Determine whether to present comparative information
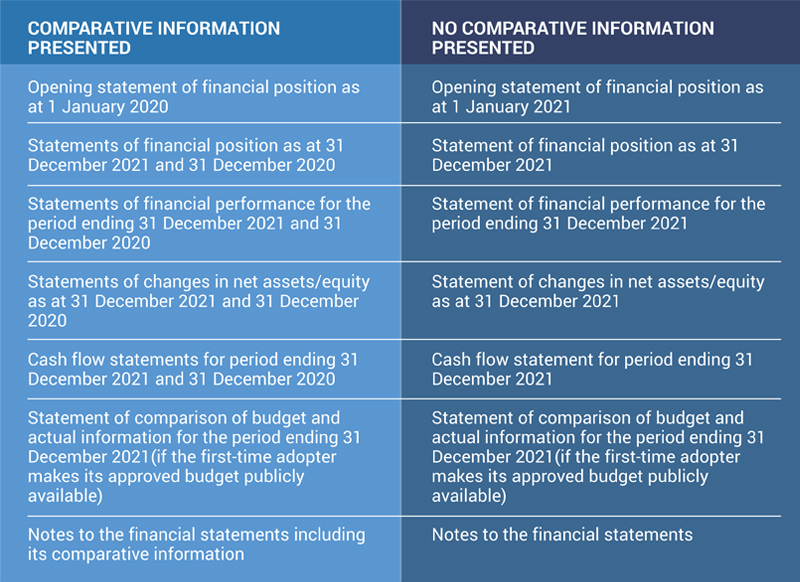
As MPSAS 33 does not require a first-time adopter to present comparative information, it can elect whether or not to present such information. This is illustrated below.

Accordingly, FSB Y should present the following whether it elects to present or not to present comparative information.
 Review of accounting policies
Review of accounting policies
The general rule is when a first-time adopter adopts MPSAS, it shall apply all the requirements of the MPSASs retrospectively subject to certain exceptions and exemptions set out in MPSAS 33. Accordingly, it needs to select relevant accounting policies, apply exceptions as well as determine whether to apply relevant exemptions. This would require a gap analysis to be performed to compare the accounting for the items and transactions under its previous basis of accounting and MPSAS.
Apply exceptions
The exceptions relate to estimates where the first-time adopter’s estimates under MPSAS should be consistent in accordance with its estimates under the previous basis of accounting (after adjustments to reflect any difference in accounting policies), unless there is objective evidence that those estimates were inconsistent with the requirements in MPSASs.
Exemptions
These are the exemptions that will not affect the fair presentation of a first-time adopter’s financial statements and its ability to assert compliance with accrual basis MPSASs during the period of transition. The first-time adopter may elect to use one or more of the available exemptions⁴. It shall not apply these exemptions by analogy to other items.
Prepare an opening statement of financial position
In its opening MPSAS statement of financial position, the first-time adopter should:
- recognise all assets and liabilities whose recognition is required by MPSASs;
- not recognise items as assets or liabilities if MPSASs do not permit such recognition;
- reclassify items that it recognised in accordance with its previous basis of accounting as one type of asset, liability or component of net assets/equity, but are a different type of asset, liability or component of net assets/equity in accordance with MPSASs; and
- apply MPSASs in measuring all recognised assets and liabilities.
As the accounting policies that an entity uses in its opening MPSAS statement of financial position differ from those that it used for the same date using its previous basis of accounting, all adjustments resulting from the application of MPSASs to the opening MPSAS statement of financial position are recognised in accumulated surplus or deficit (or, if appropriate, another category of net assets/equity) at the date of adoption.
Identify disclosures required
MPSAS 33 also requires compliance with all of the disclosure requirements of other MPSASs and imposes additional disclosure requirements specific to the first MPSAS financial statements or transitional MPSAS financial statements. In particular, a first-time adopter is required to provide reconciliations between amounts reported under its previous accounting policies and the equivalent measures under MPSASs.
¹ The date an entity adopts MPSASs for the first time and is the start of the reporting period in which the first-time adopter adopts MPSASs and for which the entity presents its first transitional MPSAS financial statements or its first MPSAS financial statements.
² The first annual financial statements in which an entity complies with MPSASs and can make an explicit and unreserved statement of compliance with those MPSASs because it adopted one or more of the transitional exemptions in MPSAS 33 that do not affect the fair presentation of the financial statements and its ability to assert compliance with accrual basis MPSASs.
³ The financial statements prepared in accordance with MPSAS 33 where a first-time adopter cannot make an explicit and unreserved statement of compliance with other MPSASs because it adopted one or more of the transitional exemptions in MPSAS 33 that affect the fair presentation of the financial statements and its ability to assert compliance with accrual basis MPSASs
⁴ Refer to paragraphs 64 to 134 of MPSAS 33 for the exemptions available.
Rasmimi Ramli is the Deputy Executive Director, Digital Economy, Reporting & Risk (DERR) Division, MIA







