By SMP Department, Professional Practices & Technical
This article explores the development and implementation of Audit Quality Indicators (AQIs) as an important tool in assessing and improving audit quality in the public practice sector. It starts with an overview of the international landscape of AQIs, highlighting variations in approaches, transparency, and the nature of information. It also delves into Malaysia’s specific initiatives for audit firms on AQIs.
The concept of enhancing audit quality by focusing on AQIs emerged from the Strategic Paper to Strengthen the Public Practice Sector and SMPs proposed by the Public Practice Committee (PPC) in 2022. The primary objective is to offer insights into factors influencing audit quality, enabling audit firms to identify and address past failings and ongoing challenges promptly.
International Development on AQIs
Internationally, audit regulators, audit firms and professional bodies have attempted to add transparency to audit quality by advocating the use of AQIs. AQI initiatives differ quite significantly throughout different countries worldwide (see Table 1).
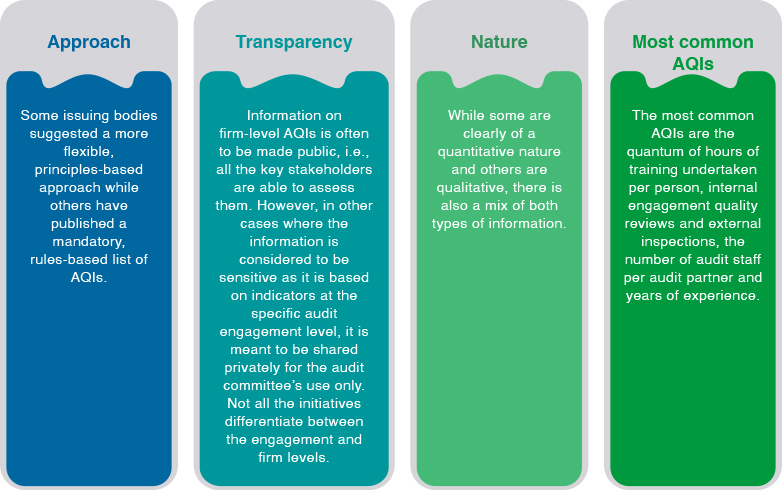
Source: Overview of Audit Quality Indicators Initiatives, July 2016, Federation of European Accountants.
Table 1: Overview of Audit Quality Indicators Initiatives

Note: Compiled by MIA’s SMP Department from various sources
AQIs and ISQM
ISQM 1 requires a proactive and tailored approach to quality management. It focuses on achieving quality objectives through identifying risks to those objectives and responding to the risks. According to the ISQM 1, a system of quality management addresses the following eight components:
- The firm’s risk assessment process
- Governance and leadership
- Relevant ethical requirements
- Acceptance and continuance of client relationships and specific engagements
- Engagement performance
- Resources
- Information and communication
- The monitoring and remediation process
A firm’s risk assessment process and monitoring and remediation process set out specific procedures that the audit firm is required to follow. The remaining components comprise specific quality objectives the audit firm is required to establish. Audit firms’ key performance indicators and AQIs determined by different organisations usually fall into one or more of these components.
Within the International Standard on Quality Management (ISQM) framework, AQIs provide critical insights necessary for managing and improving audit quality effectively. They help to enhance the robustness of the quality management system, ultimately leading to higher standards of audit practice. By leveraging AQIs, firms can continuously monitor and enhance their processes, enabling them to meet the evolving standards of auditing.
Continuous Improvement: Both ISQM and AQIs emphasise continuous improvement. ISQM requires firms to regularly review and improve their quality management system, and AQIs provide the data needed to inform these improvements. By analysing AQIs, firms can make data-driven decisions to enhance audit quality and address emerging risks.
Quality Management System Integration: ISQM 1 requires firms to establish a quality management system that includes identifying quality objectives, assessing quality risks, and implementing responses to address those risks. AQIs are integral to this system as they provide measurable data that firms can use to assess whether their quality objectives are being met and to identify areas where quality risks may exist.
Monitoring and Evaluation: AQIs serve as a key component in the monitoring and evaluation processes required by ISQM. Firms use AQIs to continuously monitor the effectiveness of their quality management system and to evaluate whether it is functioning as intended. This ongoing evaluation helps firms to identify deficiencies and take timely corrective actions.
Transparency and Accountability: ISQM promotes transparency and accountability in audit practices. AQIs support this by offering a clear, measurable way to report on the quality of audit engagements. This transparency helps build trust with stakeholders, including clients, regulators, and the public.
Risk Assessment and Response: ISQM 1 involves a detailed risk assessment process to identify factors that could affect audit quality. AQIs provide specific metrics that can highlight potential risk areas, enabling firms to respond effectively. For instance, high staff turnover rates (an AQI) might indicate a risk to audit quality that the firm needs to address.
Despite the diverse practices around the world regarding the nature of reporting, intended users and characteristics of AQIs, these practices afford useful reference points for structuring and appreciating Malaysia’s specific initiatives and future efforts regarding AQIs. These initiatives target both audit firms registered with the Audit Oversight Board (AOB) and non-registrants, demonstrating Malaysia’s commitment to enhancing audit quality through tailored AQI implementation, which will be further elaborated in Part 2 of this article.







